Offshore, nearshore, and onshore software development - what's the difference?
Choosing the best way to source talent and deciding who will handle your software project is a crucial task for any organization. Unless you want the process to become a nightmare, the process of hiring IT talent and scaling up your development efforts will need a strategy. Hiring a team can be as easy or as hard as you make it - it all depends on choosing the right approach.
The main question is usually as straightforward as whether to hire software developers, testers, PMs and other IT experts to join your own in-house team, or sign a contract with an outsourcing vendor to handle the tasks related to development and testing. Another thing to work out is what location to choose in either case
Read about experience with a dedicated development team from Ukraine
Knowing all the possible options can help you to make the right choice when it comes to finding programming experts. Before starting to describe the possible models of supplementation, we first need to have a closer look at the key aspects differentiating these models. They can be narrowed down to two main issues: who will work on the project and where the development will be performed.
Engagement models for scaling the software development process
| Onshore: Same country |
Nearshore: Close/bordering country |
Offshore: Distant locations |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Proprietary sourcing |
|
|
|
| Domestic outsourcing | Nearshore outsourcing | Offshore outsourcing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Third party - outsourcing |
|
|
|
In terms of distance and location, software development activities can be divided into the categories of onshoring, nearshoring and offshoring. While this classification takes into consideration only the geographical principle, all these types of development can be performed either by the company itself, or by a third party hired to handle the creation of the product; the second option is known as outsourcing. Outsourcing comes in all shapes and sizes and the list of its types grows by the year.
In the broadest sense, outsourcing means contracting with a third-party service provider for the management and completion of a certain amount of work, for a specified length of time, cost, and level of service. While these criteria apply to all business processes equally, software development is a key example.
IT outsourcing does not require advertising - the numbers speak for themselves. Just to help you conceptualize the scale of this model, during only the first three months of 2017, businesses in Britain have spent £1.74 billion on IT outsourcing.
The most popular outsourcing models include dedicated teams, time and material model, fixed price model, team/staff augmentation, and hiring freelancers.
The term which describes the opposite model to outsourcing is insourcing, which is less common when speaking about acquiring talents. If an organization is not willing to involve a third party in carrying out its IT processes, the other option is to expand its proprietary domestic-based software development department, or to open an offshore subsidiary - a captive center.
Onshore
Onshoring in this context means that the development team is located inside the national borders in the same country as the user organization. Functions and processes are then often located near the customers. Organizations resort to onshore outsourcing, which is also called domestic outsourcing, when they face a lack of IT talents with the particular skills and knowledge required, due to the immense competition in large development centers, such as Silicon Valley. One advantage of this model is that it also allows them to reduce operations and labor costs to some extent, avoiding the roadblocks involved in operating processes overseas.
Organizations utilize onshore options for their software development or testing needs for a number of reasons.
Advantages of Onshoring
- mindset, language and timezone similarities
- geographical proximity – the team is easily accessible
- high quality of services
- more opportunities to keep the development process under control
- higher degree of regulatory certainty
Disadvantages of Onshoring
- cost of labor is higher than with nearshoring and offshoring
- high competition over talents and therefore a lack of skilled programming experts in this particular location
- Though there are only two main drawbacks of onshore development, for many companies they trump the benefits, making businesses turn instead to nearshoring and offshorings

Nearshore
Nearshoring is often defined as relocating a company’s development process to a neighboring country or to a foreign country that is close by. For example, setting up a development center in Ukraine can be considered nearshoring for companies in Norway or Germany.
Advantages of Nearshoring
Companies opting for nearshoring gain almost the same advantages as those who choose onshoring.
- geographical proximity which allows for convenient communication and low travel costs, as IT projects are becoming more and more developed and are often implemented in real time
- getting code written and tested in a nearshore location enables higher quality products through better control
- another perceived advantage is that working in the same or similar time zone allows for a comfortable schedule for the development team, which leads to higher productivity and the overall satisfaction of the team
- the neighboring country's culture, business, and work approach are often quite familiar to a company willing to transfer its IT to another location
Disadvantages of Nearshoring
Along with the merits, nearshoring also poses a different set of challenges:
- it's more difficult to provide the necessary level of data and information security, which is especially true for nearshore outsourcing, as the handling of confidential material is often an integral part of creating products
- communication is not as smooth as with onshoring, with no face-to-face meetings, and work calendars may differ, because of different holiday schedules, for example

Read about the pros and cons of having a nearshore team in Eastern Europe
Offshore
Offshoring involves the relocation of software development processes to a lower-cost location - a distant country outside of the national borders. The term offshoring is often used interchangeably with outsourcing, although it is actually only a subset of it. This may be because this model gets more attention in the media. Still, you rarely hear someone saying offshore outsourcing when they’re talking specifically about sending development jobs overseas, as it sounds excessive. By offshoring, people frequently mean outsourcing or setting up development centers in Asia, since it is far enough away from both Europe and the USA, where the largest tech companies and clients have their headquarters.
Read how to evaluate an offshore outsourcing vendor
Advantages of Offshoring
These key drivers are sometimes used interchangeably to justify the use of offshoring:
- offshoring gives organizations the opportunity to improve the cost structure considerably, due to lower labor and operational costs, which typically make up the largest portion of the production costs. Although the gap between wages of programmers in the IT industry is gradually narrowing, the difference is still significant. A recent study published by the data science team at Hired shows that software engineers based in the U.S. tend to have much higher salaries than their global counterparts. The numbers provided by Accelerance confirm this tendency.
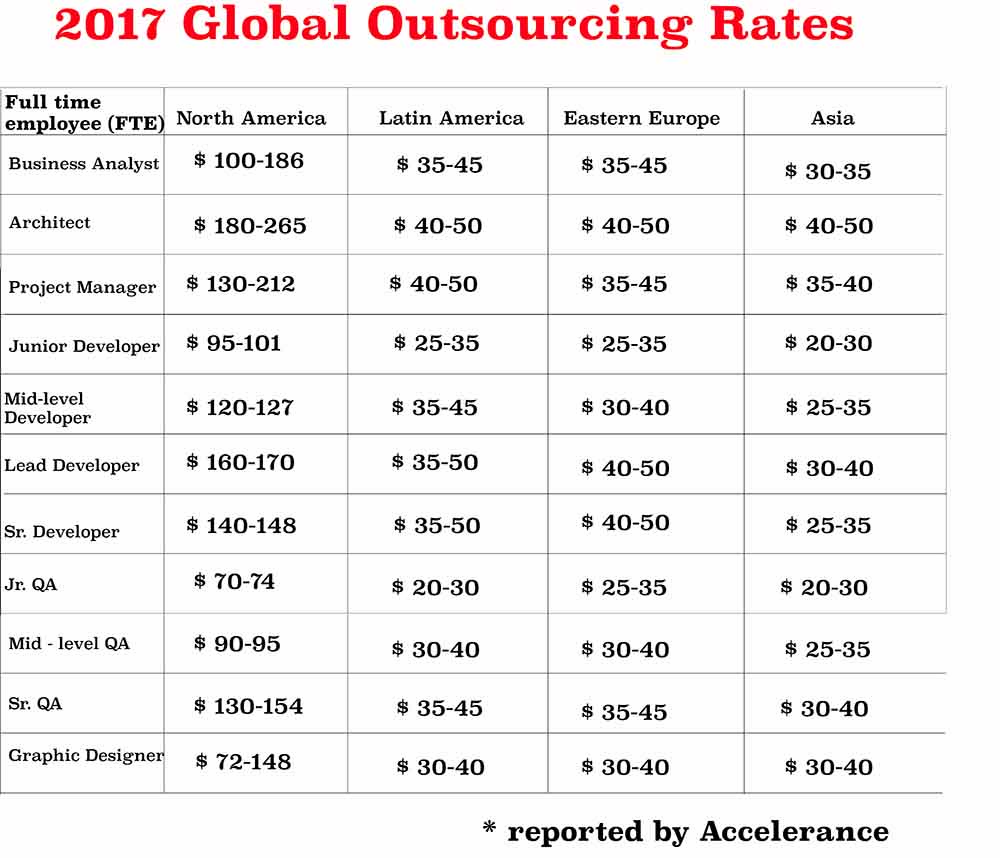
- large pool of skilled IT talent. Outsourcing gives access to large developed and mature IT markets
- external providers have long-term expertise in different areas of technology, which can be especially important to organizations starting to develop a new branch of information technology, or startups where processes and approaches are not so well-established
- the offshore model is a viable option for companies looking to carry out software development around the clock, which is also known as the "follow the sun model". Since the teams involved in creating the software product are located in different time zones, the process is being carried out almost 24/7
Disadvantages of Offshoring
- your offshore processes, whether outsourced or your own, will be influenced by the political climate in the host country
- poor communication and language barriers, among other obstacles, can get in the way of building efficient relationships. Although knowing English language is considered almost a gold standard in the IT outsourcing industry, as it is often used as a universal language for communicating with core team and managers, it may come with a certain level of misunderstanding or “distortion of information”. This mostly occurs in cases where English is not the native language of either party – the client or the offshore vendor.
- information and data security issues. This factor correlates with the reliability and reputation of the outsourcing services provider. The less reliable a company, the more chance there is of data security being compromised. So the question of providing security for the client's most sensitive personal or regulated data should be paid the closest attention during the contract negotiation process at the very start of collaboration.
- what is a positive in one case may turn out to be a problem in another: time zone differences can lead to the situation where there are only 1-2 hours, if any, of overlap between client and offshore teams.

So should a company stick to just one of the aforementioned models? It depends on the situation. There are businesses, even large ones, that prefer to contract all their software development processes or their components to one outsourcing vendor, or to set a subsidiary in only one location outside of their main office. It's easier to manage such a remote team, you don't have to keep in mind all the peculiarities of each location or coordinate multiple teams. However, many companies adhere to diversified sourcing models to meet their IT demands.
Next, we will look in greater detail at the types of engagement models used for scaling the software development process.
Written by Mira Gordijenko